W-Wing
If two Bi-Value Cells containing the same Candidates are connected by a Strong Links based on one of these Candidates, then the other common Candidate can not be the solution in any Cell that sees both Bi-Value Cells.
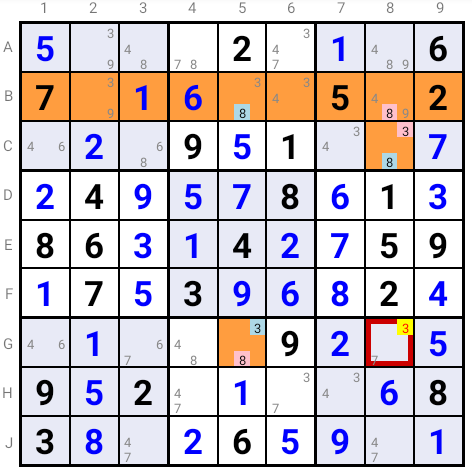
In the example above if candidate 3 is false in C8, then candidate 8 is true in C8, hence candidate 8 is false in B8, true in B5, false in G5
which implies that candidate 3 is the solution in G5 and thus false in G8.
Conversely, if candidate 3 is false in G5, a similar reasoning leads to candidate 3 being the solution in C8, which eliminates candidate 3 in G8.
You can practice this strategy by installing the SudokuCoach application on your Android™ device.
